1- About Ziferon
Ziferon belongs to interferon family-group beta. Interferons are proteins produced in the body naturally to defense against the threatening infections by immune system.
2- Ziferon Packaging
1 Ziferon vial containing 9.6 million international unit (300 micrograms) interferon beta-1b, 1 pre-filled syringe with solvent, 1 sterile vial adapter, 2 alcohol pad and 1 short needle packed in a small box.
- After reconstitution, each milliliter contains 250 microgram (8.0 million IU) interferon beta-1b
- 15 small boxes, 1 patient leaflet and 1 injection card packed in a large box.
The other ingredients in the powder: mannitol and human albumin. Each prefilled syringe contains 1.2 milliliter sodium chloride solution 0.54% w/v.
3- Ziferon Indication
Ziferon (interferon beta-1b) is indicated for the treatment of relapsing forms of multiple sclerosis to reduce the frequency of clinical exacerbations. Patients with multiple sclerosis in whom efficacy has been demonstrated include patients who have experienced a first clinical episode and have MRI features consistent with multiple sclerosis.
4- Use in specific populations
Pregnancy:
Data from available pregnancy registries have not observed an increased risk or pattern of major birth defects, preterm birth, or decreased birth weight following maternal use of interferon beta-1b. In most cases, therapy was stopped during the first trimester after pregnancy was detected. In general, disease-modifying therapies for multiple sclerosis (MS) are not initiated during pregnancy, except in females at high risk of MS activity. When disease-modifying therapy is needed in females planning a pregnancy (eg, high risk of disease reactivation), interferon beta-1b may be considered until pregnancy is confirmed, and in select cases (e.g., women with active disease), use may be continued during pregnancy.
Lactation:
There are no data on the presence of Ziferon in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for Ziferon and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Ziferon or from the underlying maternal condition.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and efficacy in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use:
Clinical studies of Ziferon did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently than younger patients.
- Contraindications:
Ziferon is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to natural or recombinant interferon beta, Albumin (Human), or any other component of the formulation.
Documentation of allergenic cross-reactivity for interferons is limited. However, because of similarities in chemical structure and/or pharmacologic actions, the possibility of cross-sensitivity cannot be ruled out with certainty.
Interferons should not be used in patients with decompensated liver disease and current severe depression and/or suicidal ideation.
Tell your doctor if any of the above applies to you.
5-Talk to your doctor before you start using Ziferon:
Pregnant mothers
- You have or have had depression (sinking feeling or sadness), anxiety (feeling uneasy, nervous, or fearful for no reason) or trouble sleeping
- You have or have had liver problems
- You have or have had blood problems such as bleeding or bruising easily, low red blood cells (anemia) or low white blood cells
- You have or have had seizures
- You have or have had heart problems
- You are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
- You are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Ziferon passes into your breast milk.
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Call your doctor, if you experienced the followings:
- If you experience symptoms such as itching all over your body, swelling of your face and/or your tongue or sudden shortness of breath. These maybe symptoms of a serious allergic reaction (hypersensitivity), which may become life threatening.
- If you feel noticeably sadder or hopeless than before the treatment with the medicine, or if you develop thoughts of suicide. If you become depressed while you are on Ziferon, you may need special treatment and your doctor will closely monitor you and may also consider stopping your treatment. If you suffer from severe depression and/or suicidal thoughts, you will not be treated with interferon family.
- If you notice any unusual bruising, excessive bleeding after injury or if you seem to be catching a lot of infections. These may be symptoms of a fall in your blood cell count or in the number of platelets in your blood (cells, which help the blood to clot). Your doctor will monitor your treatment carefully.
- If you have loss of appetite, fatigue, feeling sick, repeated vomiting, nausea, especially, if you notice widespread itching, yellowing of the skin or of the whites of the eyes, or easy bruising. These symptoms may suggest problems with your liver. The most serious liver problems were reported in patients taking other medicines or who were suffering from diseases that can affect the liver (e.g. alcohol abuse, severe infection).
- If you experience symptoms like irregular heartbeat, swelling such as of the ankles or legs, or shortness of breath. This may suggest a disease of the heart muscle. If you have had history of heart problems, inform your doctor.
- If you notice pain in your belly which is radiating to your back, and/or you feel sick or have a fever. This may suggest an inflammation of the pancreas (pancreatitis).
6- Warning and Precautions
- Hepatic Injury:
Severe hepatic injury including cases of hepatic failure, some of which have been due to autoimmune hepatitis, has been rarely reported in patients taking interferon beta. In some cases, these events have occurred in the presence of other drugs or comorbid medical conditions that have been associated with hepatic injury. Consider the potential risk of Ziferon used in combination with known hepatotoxic drugs or other products (e.g., alcohol) prior to Ziferon administration, or when adding new agents to the regimen of patients already on Ziferon. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hepatic injury. Consider discontinuing Ziferon if serum transaminase levels significantly increase, or if they are associated with clinical symptoms such as jaundice. Asymptomatic elevation of serum transaminases is common in patients treated with Ziferon. Monitor liver function tests.
- Anaphylaxis and Other Allergic Reactions:
Anaphylaxis has been reported as a rare complication of Ziferon use. Other allergic reactions have included dyspnea, bronchospasm, tongue edema, skin rash and urticaria. Discontinue Ziferon if anaphylaxis occurs.
- Depression and Suicide:
Depression and suicide have been reported to occur with increased frequency in patients receiving interferon beta products, including Ziferon. Advise patients to report any symptom of depression and/or suicidal ideation to their healthcare provider. If a patient develops depression, discontinuation of Ziferon therapy should be considered.
- Congestive Heart Failure:
Monitor patients with pre-existing congestive heart failure (CHF) for worsening of their cardiac condition during initiation of and continued treatment with Ziferon. While beta interferons do not have any known direct-acting cardiac toxicity, cases of CHF, cardiomyopathy, and cardiomyopathy with CHF have been reported in patients without known predisposition to these events, and without other known etiologies being established. In some cases, these events have been temporally related to the administration of Ziferon. Recurrence upon rechallenge was observed in some patients. Consider discontinuation of Ziferon if worsening of CHF occurs with no other etiology.
- Injection Site Necrosis and Reactions:
Typically, Injection site necrosis (ISN) occurs within the first four months of therapy, although postmarketing reports have been received of ISN occurring over one year after initiation of therapy. The necrotic lesions are typically 3 cm or less in diameter, but larger areas have been reported. Generally, the necrosis has extended only to subcutaneous fat, but has extended to the fascia overlying muscle. In some lesions where biopsy results are available, vasculitis has been reported. For some lesions, debridement, and/or skin grafting have been required. In most cases healing was associated with scarring. Whether to discontinue therapy following a single site of necrosis is dependent on the extent of necrosis. For patients who continue therapy with Ziferon after injection site necrosis has occurred, avoid administration of Ziferon into the affected area until it is fully healed. If multiple lesions occur, discontinue therapy until healing occurs. Periodically evaluate patient understanding and use of aseptic self-injection techniques and procedures, particularly if injection site necrosis has occurred.
- Leukopenia:
Monitoring of complete blood and differential white blood cell counts is recommended. Patients with myelosuppression may require more intensive monitoring of complete blood cell counts, with differential and platelet counts.
Thrombotic Microangiopathy:
Cases of thrombotic microangiopathy (TMA), including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome, some fatal, have been reported with interferon beta products, including Ziferon. Cases have been reported several weeks to years after starting interferon beta products. Discontinue Ziferon if clinical symptoms and laboratory findings consistent with TMA occur, and manage as clinically indicated.
- Flu-like Symptom Complex:
In controlled clinical trials, the rate of flu-like symptom complex for patients on interferon beta-1b was 57%. The incidence decreased over time, with 10% of patients reporting flu-like symptom complex at the end of the studies. The median duration of flu-like symptom complex in Study 1 was 7.5 days. Analgesics and/or antipyretics on treatment days may help ameliorate flu-like symptoms associated with Ziferon use.
- Seizures:
Seizures have been temporally associated with the use of beta interferons in clinical trials and postmarketing safety surveillance. It is not known whether these events were related to a primary seizure disorder, the effects of multiple sclerosis alone, the use of beta interferons, other potential precipitants of seizures (eg, fever), or to some combination of these.
- Drug-induced Lupus Erythematosus:
Signs and symptoms of drug-induced lupus reported in Ziferon-treated patients have included rash, serositis, polyarthritis, nephritis, and Raynaud’s phenomenon. Cases have occurred with positive serologic testing (including positive anti-nuclear and/or anti-double-stranded DNA antibody testing). If Ziferon-treated patients develop new signs and symptoms characteristic of this syndrome, Ziferon therapy should be stopped.
- Monitoring for Laboratory Abnormalities:
In addition to those laboratory tests normally required for monitoring patients with multiple sclerosis, complete blood and differential white blood cell counts, platelet counts and blood chemistries, including liver function tests, are recommended at regular intervals (one, three, and six months) following introduction of Ziferon therapy, and then periodically thereafter in the absence of clinical symptoms.
7- Ziferon and other medicines
- Cladribine: May enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Interferons (Beta). Specifically, the risk for lymphopenia may be increased. Risk X: Avoid combination
- Zidovudine: Interferons may enhance the adverse/toxic effect of Zidovudine. Interferons may decrease the metabolism of Zidovudine. Risk C: Monitor therapy
8-Dosing and Administration
Always use this medicine exactly as your doctor has told you for more effective treatment.
The recommended dose for sub-cutaneous (under the skin) injection in MS patients is:
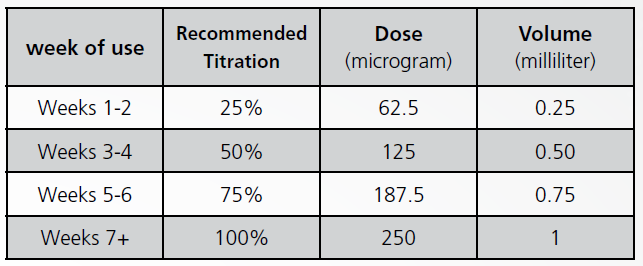
- Adults – Generally, 250 microgram (1.0 milliliter) every other day. (See the table below for dose titration).
- Efficacy and safety of the medicine has not been investigated in children and adolescents less than 18 years of age in comparison to others.
Important note:
When starting treatment with Ziferon even you have had history usage of interferon beta-1b manufactured by another company, the following table for dose titration is recommended:
9- If you forget to use Ziferon
If you have forgotten to give yourself an injection at the right time, do it as soon as you remember and then follow on with the next one 48 hours later. It is preferred to inject Ziferon at a regular time for example at evenings.
Note: You are not permitted to stop treatment without your doctor order.
- Inform your doctor if you injected too much the medicine or injected it too often.
10- How to use Ziferon
Study the procedure described below carefully and pay attention to the notices before injection:
- Prepare everything you may need in injection procedure.
- Wash your hands with a soap and water thoroughly. Do not touch your hair and skin afterwards.
- Do not touch the short needle to keep it sterile during preparation procedure.
Proper preparing procedure
- Take out the Ziferon kit from refrigerator. Leave it for 1 hour until reaches the room temperature. This will decrease pain in the injection site.
- Remove the protective cap from the Ziferon vial. Do not touch top of the vial after removing the cap.
- Use an alcohol pad to clean the top of the vial. Move in one direction and then leave the alcohol pad on top of the vial until you are ready to use it.
- Open the pack containing the adapter, but leave the adapter inside. Do not remove or touch the adapter to keep it sterile.
- Remove the alcohol pad from the top of the Ziferon vial. Place the pack containing the adapter on top of the vial. Push it down until it snaps into place. Make sure of snapping into place with pushing it down again. If you do not perform this step properly, leakage can occur and you may lose your medicine.
- Pick up the prefilled syringe from the box and untwist it by turning the plastic cap. (Syringe tip should not touch the surrounding).
- Remove the package from the adapter.
- Keep the adapter by your thumb and forefinger and twist the syringe on the adapter by your other hand. Make sure that the syringe stays firmly on the adapter.
- Transfer the prefilled syringe content completely (1.2 ml) into the vial.
- Keeping the syringe attached to the vial, gently swirl the vial (8 shape) until all powder has
dissolved. Avoid shaking the vial vigorously, as this will produce foam. Extra foam can reduce efficacy of the medicine. After reconstitution, there will be 250 micrograms per milliliter solution of interferon beta-1b and can be kept in refrigerator for 3 hours.
Note: Wait a while until the produced foam disappears. This can prevent loss of efficacy caused by foam forming and reduce pain in injection site.
- After reconstitution, Ziferon is clear, colorless to light yellow. Do not inject the vial content and discard the vial if the solution appears cloudy, or if floating particles are visible.
- Turn the vial- adapter- syringe upside down. Slowly pull back the plunger rod of the syringe to draw up the vial content.
- Tap the syringe gently until any air bubbles that formed rise to the top of the barrel of the syringe. Push the plunger rod down gently to empty the bubbles.
- Push the plunger rod down slowly to the required volume (printed digits on the syringe body) as directed by your doctor.
- Open the package containing a short needle, but leave its guard in place.
- Keep the adapter by your thumb and forefinger and untwist the syringe counterclockwise by other hand protecting its tip from touching the surrounding.
- Twist the short needle to the syringe immediately, by turning the guard once. Make sure that short needle stays on the syringe firmly.
- Set the syringe aside until the injection site is prepared.
11- Proper injection guide
Select an injection site as directed by your doctor and considering Ziferon injection card.
There are 8 zone for injection as below: Arms (2 areas), abdomen (2 areas), buttocks (2 areas), thighs (2 areas). Each area consists of 6 sections: upper (right & left), median (right & left), lower (right & left). See Ziferon Injection Card for details.
Note: You may experience injection site reactions when using the medicine. This can include swelling, discoloration, inflammation, and pain or hypersensitivity reaction at the injection site.
12- Useful tips to reduce the risk of getting injection site reactions
- Compliance to useful tips in the (proper preparing procedure) section (called sterile procedure) plays an important role in reducing injection site reaction.
- Take out the Ziferon kit from refrigerator. Leave it for 1 hour until reaches the room temperature. This will decrease pain in the injection site.
- Change the injection site in every new injection. Do not inject in the same section in 2 consecutive injections.
- Fill the Ziferon Injection card after each injection and make sure for compliance with the schedule in the card.
- Do not inject in area where you can feel lumps, bumps, firm knots, and pain.
- Do not inject in the skin that is discolored, indented, scabbed, or broken.
Talk to your doctor about these or any other unusual conditions you may find.
Note: Consult your doctor in case of cracks in the skin or liquid coming out from the injection site.
- To reduce reaction at the injection site, your initial injections must be done in the presence of specialized nurses for Ziferon who have the necessary information and skills. (Study steps mentioned in the section ≤proper injection under the skin≥).
- Use a cold compress few minutes before and after the injection. It can help to relieve and reduce pain at injection site.
- You must consult your doctor or specialized nurse for Ziferon, if injection site reactions or other side effects continue.
- The following tips are necessary for proper injection under the skin:
- Clean and disinfect the chosen site for injection with an alcohol pad in one direction and wait until dry. Hold the syringe containing the prescribed dose like a pencil or dart. Remove the guard from the short needle, but do not touch the needle itself.
- Gently pinch the skin together around the site, to lift it up a bit. This is necessary for proper injection under the skin.
- Stick the straight into the skin at a 90 degrees angle with a quick, firm motion.
- Using the slow steady push, inject the medicine by pushing the plunger rod all the way in until the syringe is empty.
- After injection, wait 15 seconds and remove the needle by pulling straight out.
- To prevent needle-stick injury and spread of infection, do not try to recap the needle.
- Place used needles, syringes, vials and alcohol pads in a closeable, puncture-resistant container such as special containers for hospital wastes, plastic bottles and an empty coffee can.
13- Adverse effects
Along with its needed effects, a medicine may cause some unwanted effects.
More common (>10%):
Peripheral edema
Skin rash
Abdominal pain
Urinary urgency
Decrease in absolute neutrophil count, leukopenia, lymphocytopenia
Increased serum alanine aminotransferase
Antibody development
Inflammation at injection site, injection site reaction, pain at injection site
Ataxia, chills, headache, hypertonia, insomnia, pain
Asthenia, myalgia
Flu-like symptoms
Fever
Less common (<10%):
Chest pain, hypertension
Dermatologic disorder
Impotence, uterine hemorrhage
Lymphadenopathy
Increased serum aspartate aminotransferase
Hypersensitivity reaction at injection site, residual mass at injection site, swelling at injection site, tissue necrosis at injection site
Malaise
Dyspnea
Rare (<1%):
Suicidal ideation
Note: If you get any serious side effects, talk to your doctor, pharmacist or nurse. This includes any possible side effects not listed in this leaflet. At the beginning of treatment adverse reactions are common but they usually will be tolerating with further treatment and do not need any medical attention. Your doctor will tell you some recommendations to minimize common adverse effects. Flu-like symptoms and injection site reactions are both common adverse effects at the start of Ziferon treatment but they usually decrease or go away over time. In general, they usually do not need any medical attention and subside with more Ziferon administration. Some points to reduce common adverse effects (Flu-like symptoms):
- Consider injecting Ziferon at bed or use of analgesics and/or antipyretics before or after Ziferon administration (according to your doctor recommendations) may be helpful to diminish Flu-like symptoms.
- Gradual dose titration according to titration table at the beginning of treatment (in Dosage & Administration section 8) may be reduced Flu-like symptoms.
14- Storage of Ziferon
- Keep Ziferon in a refrigerator (2 to 8 degrees of centigrade).
- Do not freeze.
- After adding of solvent to Ziferon powder, you can keep the prepared solution for use for 3 hours in a refrigerator.
- Ziferon has no preservative and should be used immediately after preparation. (Single use only)
- After preparation, your solution is transparent (colorless to light yellow). Do not inject and discard the vial if the solution appears cloudy, or if floating particles are visible.
15- Nurse-Patient Helpline Team
You can contact Drugs Expert Consultation Center at 0935 220 3041-4 to get answers to your inquiries and also get to know nursing support centers in your city. Expert Consultation Center is always ready to answer the questions of our valued customers.



