Safety and efficacy comparison of Ziferon® versus Betaferon® in treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis
Responsible Researchers:
Dr. M. Saeidi, Dr.M.Foroughipoor, Dr.M Salehi, Dr.B, Pourmokhtari
Mashhad Medical Science University
:Study design
A prospective, non-randomized, open-label, Non-Sponsored By Company clinical study conducted at Mashhad Medical University.
:Objective
To compare the clinical efficacy, as expressed by relapse rate and disability accumulation, and safety profile of Ziferon® and Betaferon®
:Participants and Schedule
60 consecutive patients with relapsing forms of MS were enrolled from the MS Mashhad Medical University out-patient clinic. After being informed in detail of the two treatment options existing at the time of the study, the patients chose by themselves to receive either: (a) Ziferon® 250 mcg subcutaneously (SC) alternate day (Ziferon®, 30 patients), or (b) Betaferon® 250 mcg SC in alternate day (30 patients). Mean relapse rate/year and mean EDSS/year were calculated for each group during the year of treatment.
:Follow-up
12 month per patient
:Study Status
on going
:Results
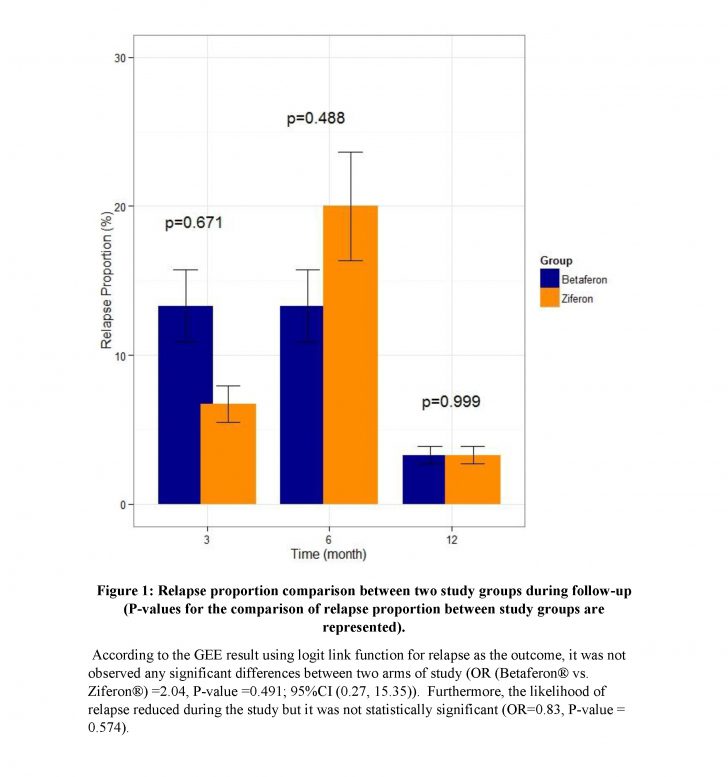
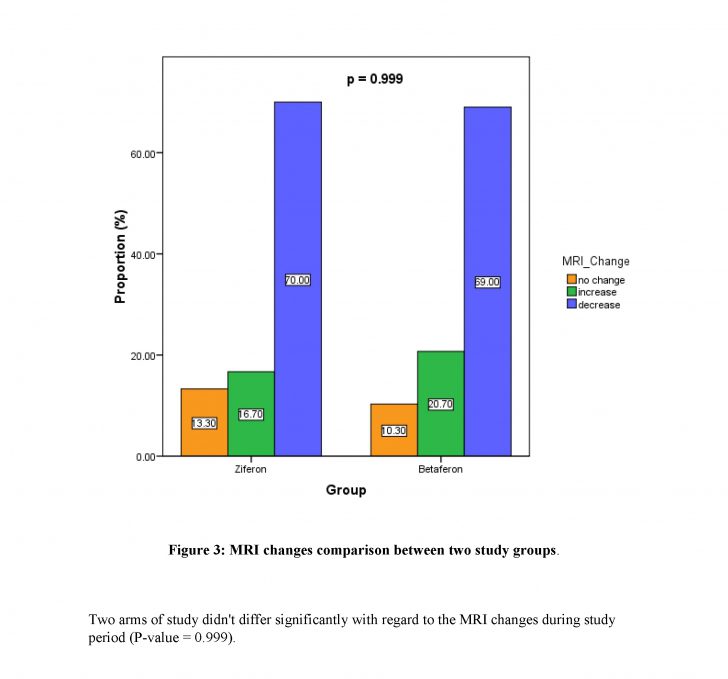
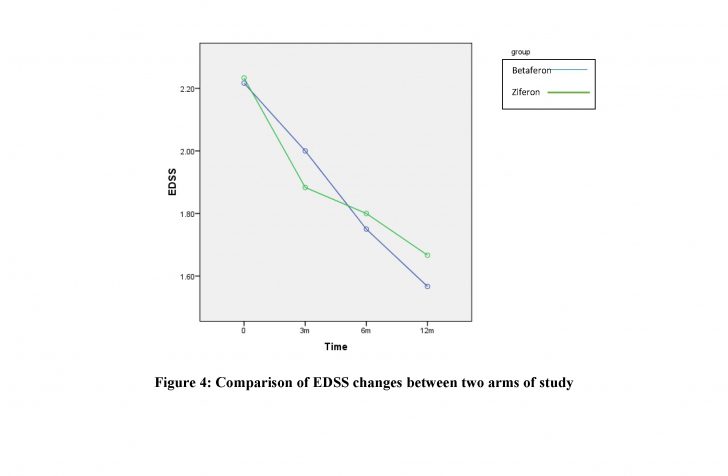
After one year follow-up of patients, no statistically significant findings were observed among the two groups regarding relapse frequency (P-value> 0.99). No significant difference was found between Ziferon® and Betaferon® groups in the proportion of improved, stable, or worsened patients or the EDSS changes (P-value= 0.97).
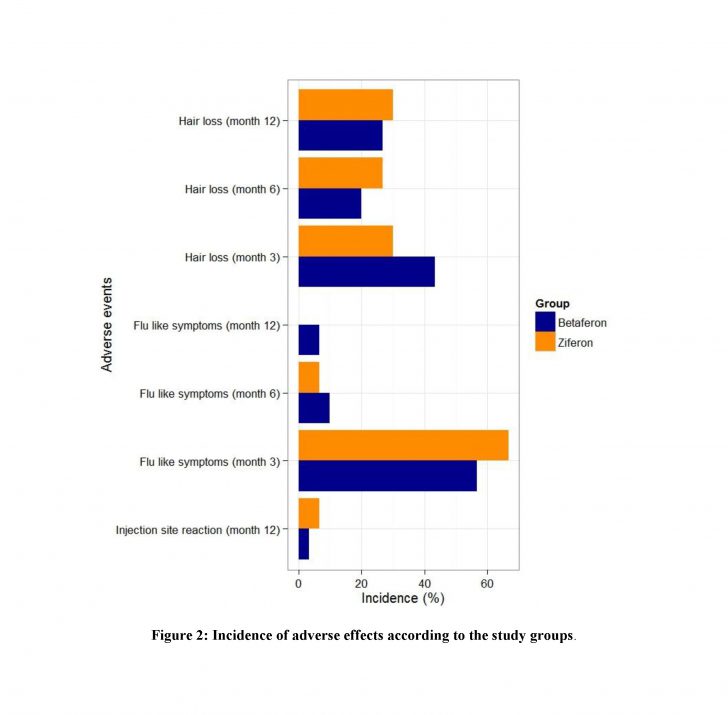
Both groups were generally well tolerated and there were no significant differences between treatment groups in the incidence of adverse events. Injection site reaction at the first 6 months after drug onset is higher in Ziferon but at the end of following period, no significant differences were observed between two arms of study (P-value > 0.99).
:Conclusions
Conclusion: The present study, despite the limitations of an open-label study, confirms that Ziferon® and Betaferon® treatment seem to be equally effective for the control of exacerbations in MS.
The adverse event profile, as reported by the patients, was also similar and no statistically significant difference was observed among the two groups regarding safety profile.
